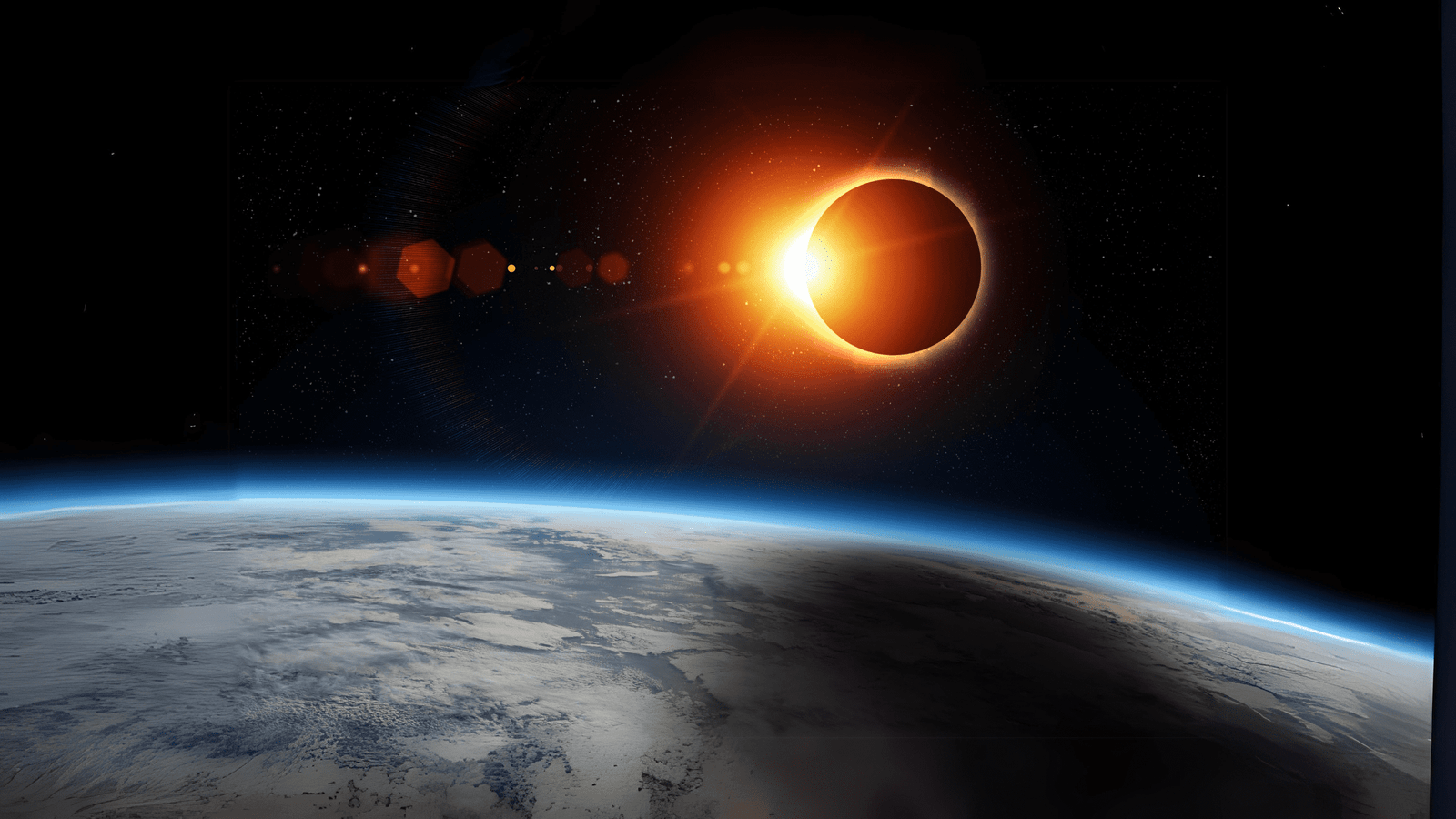
On April 8, 2024, a spectacle will unfurl across the skies: a total solar eclipse visible across parts of North America. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily cloaking regions of our planet in shadow. Unique to this event, the path of totality, where the Moon completely covers the Sun, will traverse from Mexico through the United States and into Canada, offering millions a chance to witness daytime darkness.

The total solar eclipse of 2024 is particularly significant due to its expansive path of totality, covering densely populated areas and providing an exceptional opportunity for scientific study and public engagement. Astronomical phenomena like this give researchers valuable insight into the Sun’s corona, while educators and organizations plan events to enhance public understanding of our celestial mechanics. Preparation is key for those aspiring to experience the eclipse, as proper eye protection is mandatory to safely view the Sun’s obscured disk.
Key Takeaways
- The total solar eclipse of 2024 will pass through North America on April 8.
- Wide visibility makes it notable for public viewing and scientific research.
- Safe viewing requires planning and the correct protective gear.
Table of Contents
Fundamentals of Solar Eclipses

Solar eclipses are phenomena during which the moon moves between the sun and the earth, temporarily blocking the sun’s light. A spectacular range of events, these eclipses can be observed from specific locations on Earth’s surface, provided that one adheres to crucial safety guidelines.
Eclipse Mechanics
Solar eclipses occur when the moon passes directly between the Earth and the sun, casting a shadow on Earth’s surface. This can only happen during a new moon phase, when the moon’s unilluminated side faces our planet. The darkest part of the moon’s shadow, the umbra, is what causes a total solar eclipse for observers within its path, while the outer shadow, or penumbra, results in a partial solar eclipse.
Types of Eclipses
Eclipses can be total, partial, or annular. During a total solar eclipse, the moon completely covers the sun, resulting in totality. In contrast, a partial solar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the sun is obscured. An annular eclipse happens when the moon covers the sun’s center, leaving a ring-like appearance.
Eclipse Science and Observation
Eclipses offer unique scientific opportunities where scientists can study the sun’s outer atmosphere, or corona, which is normally obscured by the sun’s brightness. Safe observation techniques include using a telescope with a solar filter, a pinhole projector, or eclipse glasses designed to protect the eyes from harmful sunlight.
Safety Guidelines
Safety is paramount during an eclipse; never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection. Regular sunglasses are not sufficient; instead, one must use eclipse glasses with solar filters that meet the international safety standard, ISO 12312-2.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Eclipses have been important in history, often interpreted as omens or divine messages. Different cultures have their unique stories and traditions related to eclipses, many of which underscore the event’s significance in human society over the millennia.
Eclipse Photography Tips
Capturing an eclipse through photography requires preparation and the right equipment. Use a camera with manual settings and a telephoto lens for close-ups. A solar filter is necessary to prevent damage to both the camera sensor and the photographer’s eyes. Low ISO settings, fast shutter speeds, and small apertures will result in clear images that showcase the eclipse’s dramatic visuals.
The 2024 Solar Eclipse

The solar event of the year will occur on April 8, 2024, when a total solar eclipse will captivate viewers across North America, from the Pacific to the Atlantic.
Overview of April 8, 2024, Eclipse
The coming eclipse is a total solar eclipse, a natural phenomenon that occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow that fully obscures the Sun.
Eclipse Path and Timeline
The eclipse path will stretch from Mexico, sweeping across the United States, and into Canada. The path of totality will encompass states including Texas, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Vermont, and parts of New England before moving on through parts of Eastern Canada such as Quebec and Newfoundland. The maximum eclipse will be observed where the moon’s shadow passes closest to Earth’s center.
- Start of Totality on the Pacific coast: Approximately 11:07 a.m. PDT
- End of Totality on the Atlantic Coast: Afternoon local time
Observation Locations and Events
Many towns and cities within the path of totality will host viewing parties and educational events. NASA will also provide live streams and broadcasts for those who cannot witness the event in person.
Impact on Cities in the Path
Cities directly in the eclipse path, such as Dallas, Indianapolis, Cleveland, and Montreal, are expected to see an increase in visitors. Local businesses and tourism officials anticipate a boost from this astronomical event.
Eclipse Maps and Resources
Maps detailing the eclipse path and times are essential for anyone planning to observe this event. NASA provides comprehensive information for enthusiasts to plan their viewing experience effectively. Additionally, interactive maps show local times and weather prospects for the best observation opportunities.
Global Context and Visibility

The total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, is a significant astronomical event where the Moon will completely block the Sun, casting a shadow over certain areas of the Earth. This phenomenon provides a unique spectacle visible in particular regions worldwide.
North American Visibility
In North America, viewers across a swath of the continent will experience the full spectacle. The eclipse begins over Mexico‘s Pacific coast and makes its way through the United States, from Texas to Maine, with regions along this path witnessing total darkness as they are encompassed by the Moon’s umbra. Key locations such as Dallas, Indianapolis, Cleveland, and Buffalo are prime spots for observation. The event is notable not just for its visibility but also for the breadth of the path across North America.
Canada, although farther north, will not be left out. Regions in eastern Canada, including cities like Toronto and Montreal, can anticipate a partial eclipse, providing an impressive display despite not experiencing totality.
International Viewing
While the event will be most prominent in North America, the eclipse’s partial phases can be observed in regions outside the path of totality. Areas in Europe and South America will experience a partial solar eclipse, just to a lesser degree. Observers located in northern South America will find themselves viewing the event during the afternoon, while those in certain parts of Europe can catch the eclipse during sunset, weather and geographical location permitting.
The vast expanse of both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans will serve as witnessing grounds for this astronomical occurrence, though viewership will be confined to the realms of ships and aircraft. Areas within the Arctic Circle will miss this event, with the eclipse not being visible due to the geographical limitations set by the eclipse’s path.
Scientific Research and Opportunities

During the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, scientists are presented with an extraordinary opportunity to investigate celestial phenomena. As the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, a brief window opens for NASA and other research bodies to study the sun’s corona, which is otherwise too difficult to observe given the sun’s brightness.
- Eclipse Mechanics: The alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon provides a natural laboratory for studying the corona.
- Solar Atmosphere: The corona reveals itself in full glory during an eclipse, enabling direct observations.
NASA has selected five experiments for this event to deepen their understanding of solar dynamics. This includes using high-altitude balloons, specialized cameras, and spectrometers, which make measurements only possible during an eclipse.
| Science Teams | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Team A | Sun’s Corona Imaging |
| Team B | Atmospheric Effects |
Citizen science also plays a crucial role during eclipses. With NASA’s support, three citizen science projects will collect data to contribute to the body of knowledge on the solar atmosphere and its interactions with Earth.
Eclipses impact radio wave propagation, and scientists will harness this rare opportunity to study this effect, leveraging ham radios and other technologies. The darkening of the sky also allows for examination of Earth’s upper atmosphere and the effects of solar radiation on this layer.
Eclipse Preparation and Planning
Proper preparation is crucial to fully experience the total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024. It involves securing the right viewing equipment and planning travel and lodging in advance, especially if it includes journeying to the path of totality. Educational materials can enhance understanding and appreciation of the phenomenon.
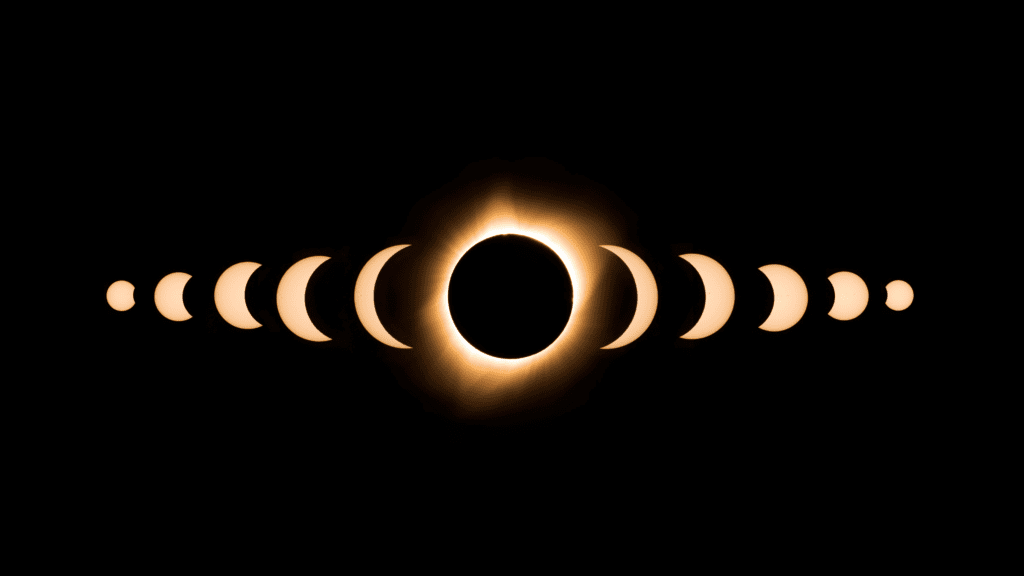

Equipment and Viewing Methods
For safe viewing, eclipse glasses or handheld solar viewers are essential. They must meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard to ensure eye protection. For a more magnified view, telescopes with solar filters or binoculars can be used, albeit with caution. The pinhole projector, a simple and safe DIY method, provides an alternative to directly observing the eclipse.
Travel Tips for Eclipse Chasers
Those planning to travel to the path of totality should book accommodation well in advance due to the high demand. Familiarity with local roads and having a backup plan will help navigate potential traffic jams on eclipse day. It’s recommended to arrive at the chosen viewing location early to secure a prime spot.
Educational Resources
NASA offers comprehensive educational resources to deepen knowledge about solar eclipses. This includes interactive content, safety instructions, and mini-lessons suited for various age groups. Taking advantage of these materials before the eclipse can greatly enrich the experience and ensure that viewers are well-informed.
Comparisons with Other Eclipses
The 2024 total solar eclipse is poised to provide a unique spectacle with its own distinctive characteristics when compared to other eclipses. This section addresses the differences in duration, visibility, and paths of totality between the 2024 event and other notable eclipses, as well as variations in the patterns and types of eclipses observed from Earth.
2024 vs. Other Total Solar Eclipses
The upcoming total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, stands apart from previous eclipses in several aspects. It contrasts notably with the highly-observed 2017 Great American Eclipse; for instance, the 2024 eclipse will have a path of totality that is significantly wider, ranging between 108 and 122 miles wide, which allows more areas to experience totality. Additionally, its maximum duration of totality will reach 4 minutes and 28.2 seconds, surpassing many of its predecessors.
Eclipse Frequency and Patterns
Solar eclipses occur roughly every 18 months, but the experience of totality in any given location is rare—often occurring centuries apart. The pattern of eclipses, explained by the Saros cycle, dictates that similar eclipses recur every 18 years, 11 days, and 8 hours. There’s a notable difference between the frequency of solar and lunar eclipses; lunar eclipses are typically more frequent.
Difference Between Solar and Lunar Eclipses
A total solar eclipse, such as the one occurring in 2024, happens when the moon entirely covers the sun, casting a shadow on Earth. In contrast, during a lunar eclipse, Earth’s shadow falls upon the full moon. While a total solar eclipse is visible only from a small area on Earth’s surface, a total lunar eclipse can be seen by anyone on the night side of Earth at the time of the eclipse, resulting in broader visibility.
Post-Event Discussions
After the 2024 total solar eclipse, researchers and enthusiasts alike converge to dissect the event. Key areas of focus include the scientific data harvested, the proliferation of images and videos shared, the anticipation of future occurrences, and the range of local events that celebrated the eclipse.
Data Analysis and Findings
Scientists meticulously examine the data collected during the eclipse to advance their understanding of solar phenomena. Insights gained can range from changes in the solar corona to fluctuations in atmospheric conditions. Research institutions and NASA often publish their findings, facilitating a deeper understanding of solar eclipses and their impacts on Earth.
Photography and Media Sharing
The eclipse spurred an outpouring of photography across various platforms, with both amateur and professional photographers sharing their captures. Social media networks buzzed with images and experiences, creating a tapestry of the event from multiple perspectives. Online forums became hotspots for enthusiasts to share tips, techniques, and the stories behind their photos.
Next Major Eclipses
Anticipation builds around when and where the next major solar eclipses will occur. Lists and detailed maps emerge outlining prospective dates and the best locations to witness these celestial events. Communities and organizations begin early preparations to host viewings and educational workshops.
Commemorations and Community Events
Local communities celebrate the 2024 eclipse through various commemorations. Events range from the release of special eclipse stamps to gatherings where participants share their eclipse stories. These community efforts underscore the unifying aspect of such a spectacular natural phenomenon.
Appendix
This appendix serves as a supplementary resource to enhance understanding of the 2024 total solar eclipse event. It provides essential terminology, links to scientific concepts, future eclipse forecasts, and a curated list of scholarly references.
Glossary of Terms
- Umbra: The darkest part of the Moon’s shadow during an eclipse, where totality is observed.
- Totality: A phenomenon during a total solar eclipse when the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon.
- Corona: The outer layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, visible during a total solar eclipse.
- Eclipse: The obscuration of one celestial body by another. In this context, referencing a solar eclipse.
Related Scientific Phenomena
Eclipses involve the interplay between the Sun, Earth, and Moon, leading to the fascinating study of celestial mechanics. Understanding this natural occurrence contributes to multiple fields of science including astrophysics and heliophysics.
Eclipse Predictions for the Future
NASA provides eclipse predictions aiding education and research. These projections are based on orbital mechanics and historical findings to anticipate upcoming solar eclipses.
References and External Links
Various credible sources offer in-depth information on solar eclipses:
- Ars Technica’s guide to viewing the total solar eclipse
- 2024 Total Eclipse overview by Science@NASA
- Interactive map and local times from timeanddate.com
- National Solar Observatory’s eclipse map for April 8, 2024
- Astronomy.com’s state-by-state guide to the 2024 eclipse
Frequently Asked Questions
The highly anticipated total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, will captivate observers across North America. This section addresses common inquiries regarding the event’s optimal observation locations, timing, visual resources, specific path details, and future occurrences.
What locations will provide the best viewing experience for the total solar eclipse in 2024?
For optimal viewing of the total solar eclipse, areas that lie within the path of totality will offer the best experience. This FAQ section provided by IN.gov gives significant insight into prime locations within Indiana.
At what time will the total solar eclipse occur on April 8, 2024?
The timing of the total solar eclipse will vary depending on geographic location. Observers can expect totality to occur around midday. This NASA FAQ offers detailed timing based on different locations across the path of totality.
Can you provide an interactive map showing the path of the 2024 solar eclipse?
Interactive maps are valuable for planning your eclipse experience. Science@NASA hosts resources that include an interactive map displaying the path the eclipse will take.
Which areas will the solar eclipse pass through in Ohio during the 2024 event?
In Ohio, the path of totality will pass through cities like Toledo and Cleveland among others, allowing residents to view the eclipse in full. The NASA eclipse page details the path, including times when the eclipse will be visible in different parts of the state.
Is there a list of future dates for total solar eclipses after 2024?
Future solar eclipses are constantly tracked, with lists available for planning observation of these celestial events past 2024. A comprehensive list can be found in various astronomy resources, including NASA’s eclipse website.
How often do total solar eclipses occur?
Total solar eclipses happen approximately every 18 months somewhere on Earth. Witnessing one from a specific location is rare, occurring about once every 375 years on average for each location on the planet.