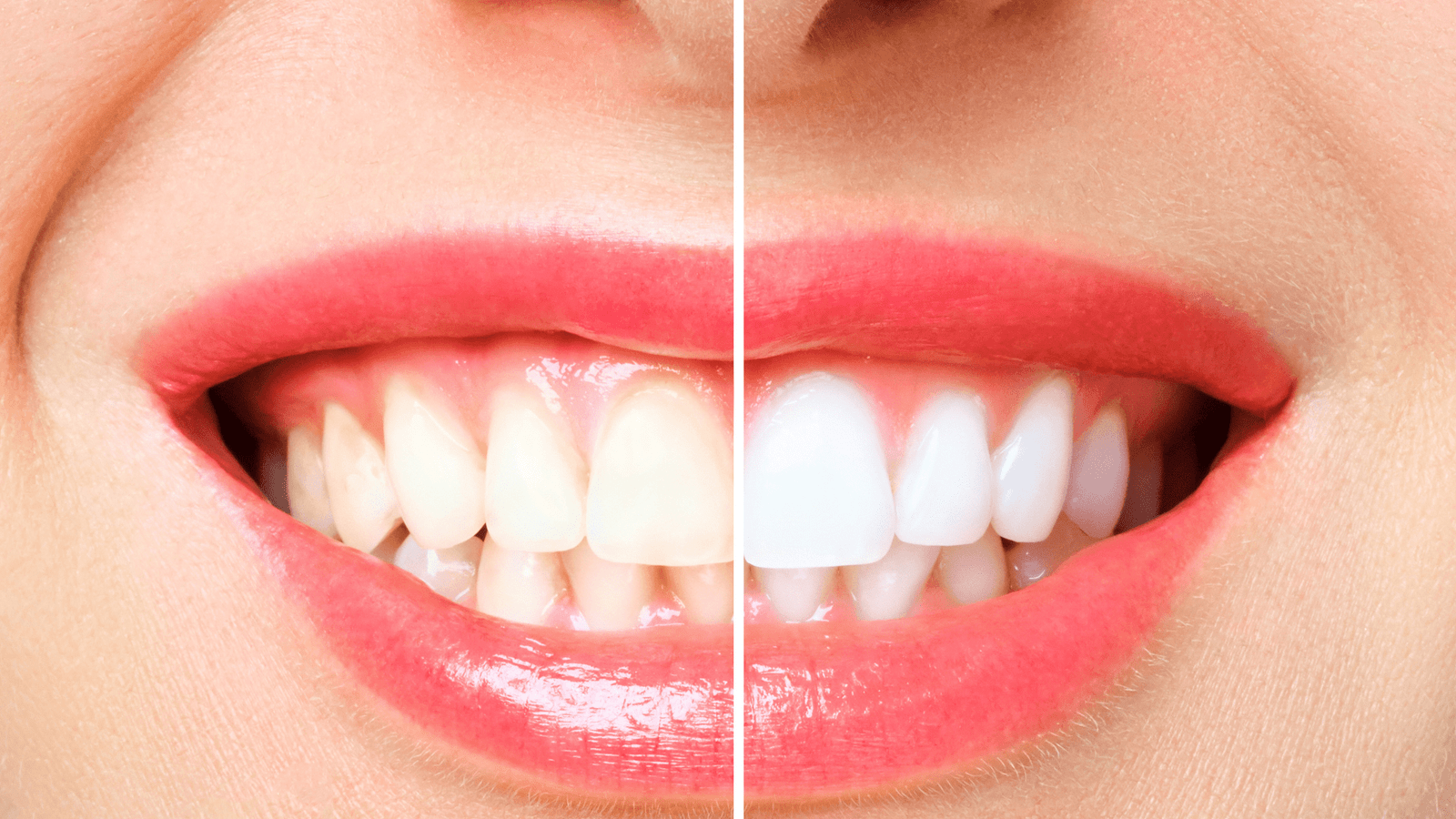
Teeth discoloration can be a sign of various underlying issues, ranging from lifestyle habits to oral hygiene. However, what isn’t often discussed is the connection between the color of one’s teeth and nutritional intake, specifically vitamin deficiencies. A lack of certain vitamins in the diet can lead to changes in tooth enamel, which may cause teeth to appear yellowed or develop white or dark spots (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency). This type of discoloration may indicate more systemic health concerns and warrants a closer look into one’s dietary habits.
Understanding how different vitamins affect dental health is crucial for maintaining a bright and healthy smile. Vitamins are essential for various bodily functions, including the maintenance of oral health. They help in the formation of enamel, the prevention of gum disease, and the overall integrity of teeth. When the body is deficient in key vitamins, such as vitamin D, C, and B vitamins, it can result in teeth that are less resilient to decay and more prone to discoloration. Ensuring a balanced diet is a fundamental step in preventing and managing dental health issues related to vitamin deficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin deficiencies can cause teeth discoloration and affect oral health.
- A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins is crucial for maintaining tooth enamel integrity.
- Addressing vitamin deficits may improve dental health and reduce discoloration risks.
Table of Contents
Understanding Teeth Discoloration

Teeth discoloration is an alteration in the color of one’s teeth that can detract from a bright, white smile. It’s critical to distinguish between the different types and causes to address the issue effectively.
Types of Tooth Discoloration
There are primarily two types of tooth discoloration: extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic discoloration is characterized by stains on the enamel, the tooth’s outer layer. In contrast, intrinsic discoloration is due to factors that affect the inner structure of the tooth, the dentin, causing it to darken or develop a yellow tint.
Extrinsic Discoloration: Typically surface stains caused by:
- Food and Beverages: such as coffee, tea, and red wine.
- Smoking: Tobacco products are known for staining the enamel.
- Plaque: Excessive plaque buildup can also lead to discoloration.
Intrinsic Discoloration: May result from:
- Aging: Over time, enamel thins, revealing the yellow hues of dentin.
- Trauma: Impact can disrupt enamel formation or damage the internal tooth structures.
Common Causes of Discoloration
The causes of teeth discoloration range from simple lifestyle choices to more complex health issues. It’s important to understand that both types of discoloration can be influenced by a variety of factors such as:
- Aging: As individuals age, enamel wears away revealing the naturally yellower dentin.
- Food and Beverages: Certain deeply pigmented foods and drinks can stain teeth.
- Smoking: A major contributor to extrinsic stains.
- Plaque: Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque accumulation which affects tooth color.
It’s vital for individuals to know not only the common causes but also that discoloration might be indicative of underlying dental or health concerns. Regular dental check-ups can help monitor and manage tooth discoloration.
Role of Vitamins in Dental Health
Vitamins and minerals are pivotal in maintaining oral health, with deficiencies often leading to problems such as tooth discoloration and enamel weakening. This section delves into the specific roles vitamins play and the consequences of their deficiency (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency) on dental health.
Impact of Vitamin Deficiency on Oral Tissues
Vitamin deficiencies (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency) can have a significant impact on the mouth’s oral tissues. A lack of Vitamin D, for example, may lead to defective tooth mineralization, resulting in enamel and dentin defects. The enamel, being the outermost layer of a tooth, is critical for protection against decay; when weakened, it may result in increased susceptibility to caries and discoloration.
Moreover, calcium deficiency can compromise the structure of the teeth and bones, since calcium is essential for their strength and density. Similarly, a deficiency in Vitamin C can cause gum inflammation and bleeding, while insufficient Vitamin A affects the maintenance of mucous membranes in the mouth, potentially leading to tissue damage and disease.
Key Vitamins for Healthy Teeth
Certain vitamins are noteworthy for their capacity to sustain dental health:
- Vitamin D: The “sunshine vitamin” is critical for healthy teeth as it facilitates calcium absorption, an essential mineral for maintaining tooth structure.
- Calcium: Found abundantly in dairy products, this mineral is vital for the development and maintenance of strong teeth and bones.
- Vitamin C: It aids in gum health and can prevent periodontal issues by strengthening the connective tissue and the walls of blood vessels in the gums.
- Vitamin A: This vitamin assists in sustaining the salivary flow and mucous membranes which are integral for a healthy oral cavity.
- Vitamin B12: Often found in fish, meat, and dairy products, a Vitamin B12 deficiency may lead to changes in the lining of the mouth and tongue, including discoloration.
In summary, for the prevention of teeth discoloration and to bolster overall oral health, a well-balanced diet rich in these vitamins is essential (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency).
Diet and Teeth Discoloration
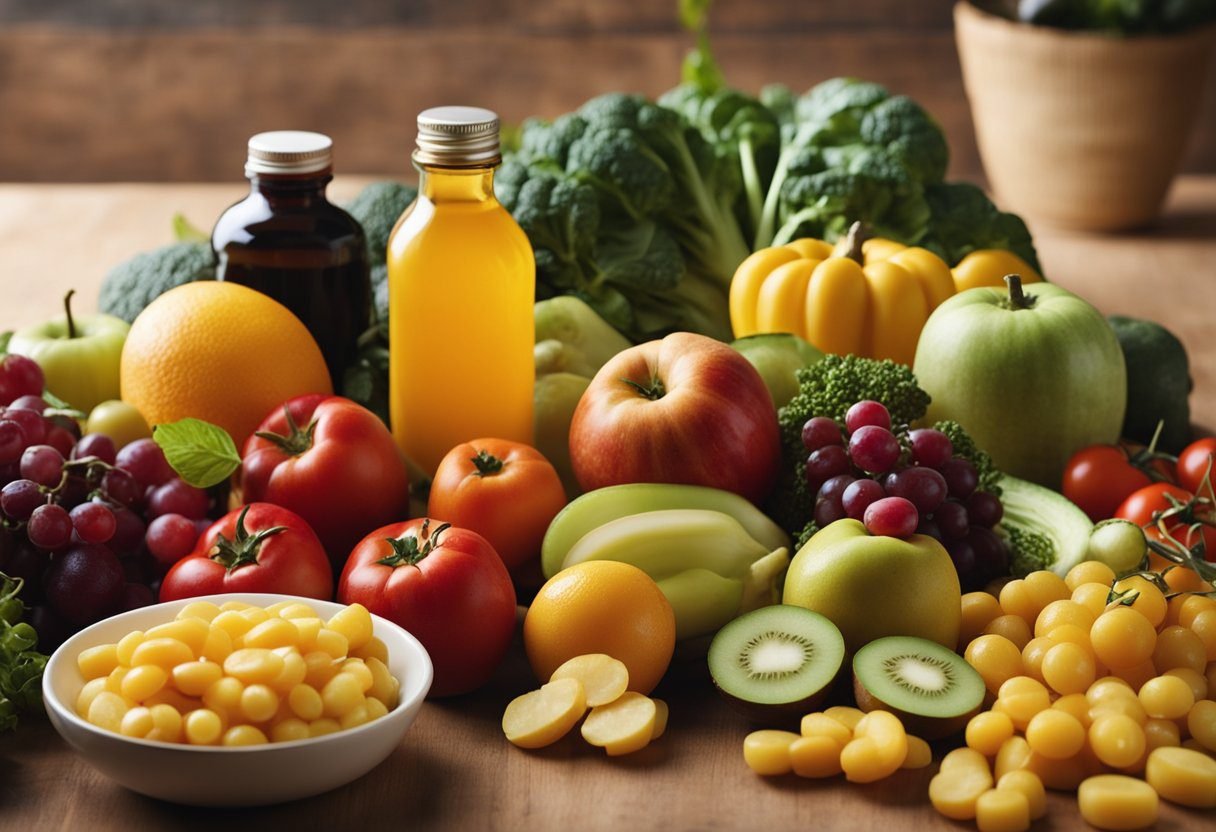

The colors on your plate could be the forecasters of your tooth coloration, with certain diets leading to discoloration while others may shield and preserve the natural whiteness of your teeth.
Foods That Cause Teeth Discoloration
Certain foods and beverages are notorious for staining teeth. Coffee and tea are at the front line of culprits, with substances called tannins that can leave behind stubborn stains. Similarly, the chromogens and acidity in red wine can discolor teeth. Regular consumption of sugar-laden foods leads to tooth decay and discoloration due to the damage caused by cavities.
Other foods like soy sauce and berries—despite their health benefits—contain pigments that cling to tooth enamel and can darken it over time. Tomato sauce, brimming with acidity, can also pave the way for other foods to penetrate the enamel, resulting in stains.
| Foods and Beverages Known to Stain Teeth |
|---|
| Coffee |
| Tea |
| Red Wine |
| Colored Sodas |
| Berries (blueberries, raspberries) |
| Tomato Sauce |
| Soy Sauce |
| Beets |
Foods That Prevent Discoloration
In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, meats, and dairy can be essential in the maintenance of tooth health and appearance. Cheese, milk, and green leafy vegetables like kale and spinach not only provide the calcium and phosphates necessary for re-mineralizing teeth but also help clear food particles and stain-causing bacteria due to their texture that increases saliva production. Crunchy fruits and vegetables, including apples and celery, act as natural stain removers by scrubbing the teeth when chewed.
Additionally, regular consumption of water not only keeps the body hydrated but also helps in washing away food debris and diluting the acids produced by oral bacteria, thereby protecting teeth from decay and discoloration.
| Foods That Can Help Maintain White Teeth |
|---|
| Cheese |
| Milk |
| Broccoli |
| Apples |
| Celery |
| Carrots |
| Pears |
| Nuts |
In conclusion, the diet plays a significant role in the color of one’s teeth, as certain foods contribute to discoloration while others can actually help prevent it. Understanding these effects can guide dietary choices to maintain a bright and healthy smile.
Prevention and Management
To combat teeth discoloration due to vitamin deficiencies (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency), one must adopt a holistic approach encompassing proper oral hygiene and consider professional teeth whitening options if necessary.
Oral Hygiene Best Practices
Implementing effective oral hygiene is crucial for maintaining dental health and preventing discoloration. A regular routine should include the use of fluoride toothpaste to help reinforce tooth enamel and reduce decay. They should brush their teeth at least twice a day and incorporate flossing to remove plaque buildup between teeth, which can lead to staining. Using an antibacterial mouthwash is also recommended to decrease bacterial growth and promote a healthier oral environment.
Professional Teeth Whitening Options
For those seeking immediate and noticeable results, professional teeth whitening performed by certified dentists could be an option. These treatments use stronger bleaching agents than over-the-counter products and can address both intrinsic and extrinsic stains effectively. For a more permanent solution to severe discoloration, individuals might explore dental bonding or veneers, which not only whiten teeth but can also correct imperfections in shape or alignment. Consulting with qualified dentists is essential to determine the best approach tailored to an individual’s specific dental needs and conditions.
Addressing Discoloration through Supplementation
Discoloration linked to vitamin deficiencies (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency) can often be addressed through targeted supplementation. A multivitamin may provide a broad range of nutrients, but individuals may require specific vitamins to tackle teeth discoloration.
Vitamin D is crucial for oral health, as it facilitates calcium absorption, important for maintaining tooth enamel. Studies suggest that a vitamin D deficiency can lead to oral health issues, including discoloration. Therefore, supplementation may be necessary, especially for individuals with limited sunlight exposure.
Calcium supplements can prove beneficial, as lack of calcium directly impacts tooth color and integrity. However, it is essential that people ensure adequate vitamin D levels to promote effective calcium absorption.
Vitamin B12 is imperative for maintaining healthy nerve cells and blood cells. A deficiency can lead to oral health problems, including teeth discoloration. B12 supplementation might be particularly necessary for vegetarians and the elderly, as they are at a higher risk of deficiency.
When considering supplementation, it is important to aim for a balanced diet as the first step. Dietary sources of vitamins are generally preferred, but in cases where diet alone is insufficient, supplements can help fill nutritional gaps. It is recommended to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation routine, as excessive intake of certain vitamins may have adverse effects.
Here’s an overview of vitamins associated with oral health:
- Vitamin D: Enhances calcium absorption.
- Calcium: Strengthens tooth enamel.
- Vitamin B12: Supports nerve and blood cell health.
Supplementation should be tailored to the individual’s nutritional needs and conducted under professional guidance to effectively address teeth discoloration (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency).
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the relationship between vitamin deficiencies and teeth discoloration, exploring specific vitamins and their impact on dental health.
What vitamin deficiencies (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency) can lead to tooth decay and weakened bones?
Vitamin D deficiency can result in a higher prevalence of periodontitis and gingival inflammation, which in turn can cause tooth decay and weakened bones.
How can one rectify calcium deficiencies affecting the teeth?
Adequate calcium intake is crucial for maintaining strong teeth and preventing osteoporosis, a condition that affects bone density and strength.
What are the symptoms of teeth cracking due to vitamin deficiency?
Symptoms can include increased tooth sensitivity, pain when chewing, and visible cracks or fractures in the teeth, often stemming from a lack of essential nutrients.
Which vitamins are known to cause teeth staining?
Vitamins are not typically direct causes of teeth staining; however, certain medications containing vitamins can lead to extrinsic tooth discoloration.
How can a deficiency in vitamin D affect the color of one’s teeth?
While vitamin D’s primary oral health role is to promote calcium absorption, severe deficiencies could lead to dental issues that indirectly affect tooth color, such as enamel hypoplasia (Teeth Discoloration Vitamin Deficiency).
What are the health conditions that may result in teeth discoloration?
Conditions such as celiac disease can lead to defects in tooth enamel, which may result in discoloration. Additionally, certain vitamin deficiencies can exacerbate dental diseases that contribute to discolored teeth.