The universe, an unfathomable expanse that stretches beyond the limits of human comprehension, serves as both a cosmic canvas and a perpetual enigma. As we embark on our exploration of “How the Universe Works,” we delve into the cosmic origins and the awe-inspiring vastness that has captivated human curiosity for centuries.
At the heart of this cosmic odyssey lies the realization that the universe is not merely a backdrop for celestial bodies; it is a dynamic entity with an intricate and evolving structure. The journey begins with the acknowledgment that the universe, with its galaxies, stars, planets, and cosmic phenomena, is a spectacle that demands both scientific inquiry and philosophical contemplation.
Table of Contents
The Structure of the Universe
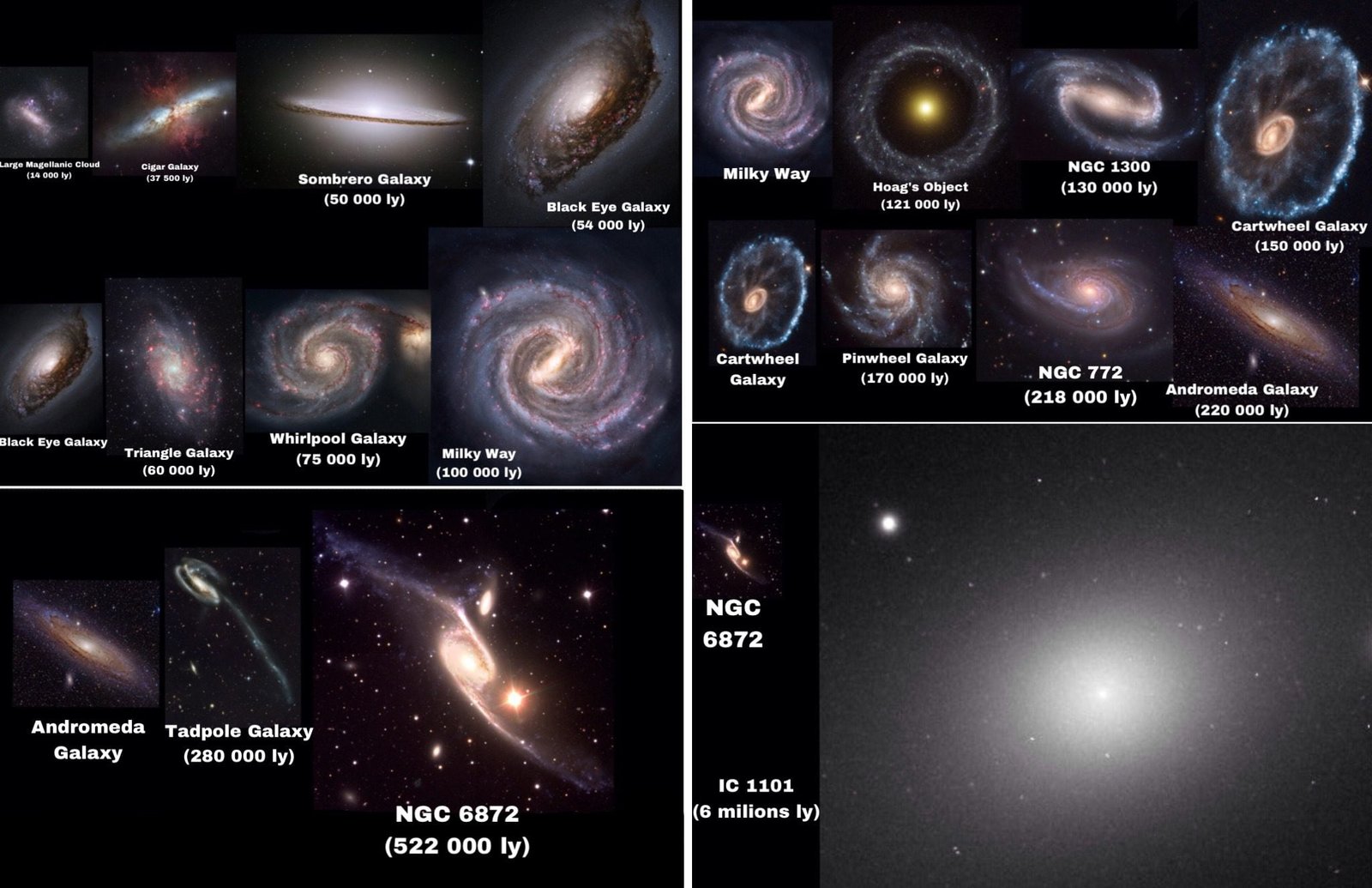

To comprehend the workings of the universe, one must first unravel its structural intricacies. Galaxies, those colossal cosmic islands, serve as the building blocks of the universe. Each galaxy, be it a majestic spiral or an elliptical giant, houses billions of stars, and collectively, they weave the cosmic tapestry.
Within these galaxies, stars take center stage. Stars, born from the gravitational collapse of vast molecular clouds, become cosmic beacons. Their life cycles, from the fiery birth in stellar nurseries to the dramatic deaths that may result in the formation of black holes or neutron stars, contribute to the dynamic nature of the cosmic landscape.
Gravity’s Role in the Cosmos
The universal force that orchestrates the celestial ballet is gravity. This omnipresent force governs the movements of celestial bodies, shaping galaxies, stars, and planets alike. Gravity is the unseen maestro directing the cosmic symphony, ensuring that each element plays its part in the grand cosmic dance.
The gravitational dance extends beyond individual galaxies. Cosmic structures, such as galaxy clusters and superclusters, emerge as gravity weaves an intricate web connecting galaxies across vast cosmic distances. Understanding gravity is not just a key to unraveling the structure of the universe; it is the very force that molds the cosmic landscape.
Celestial Bodies and their Functions
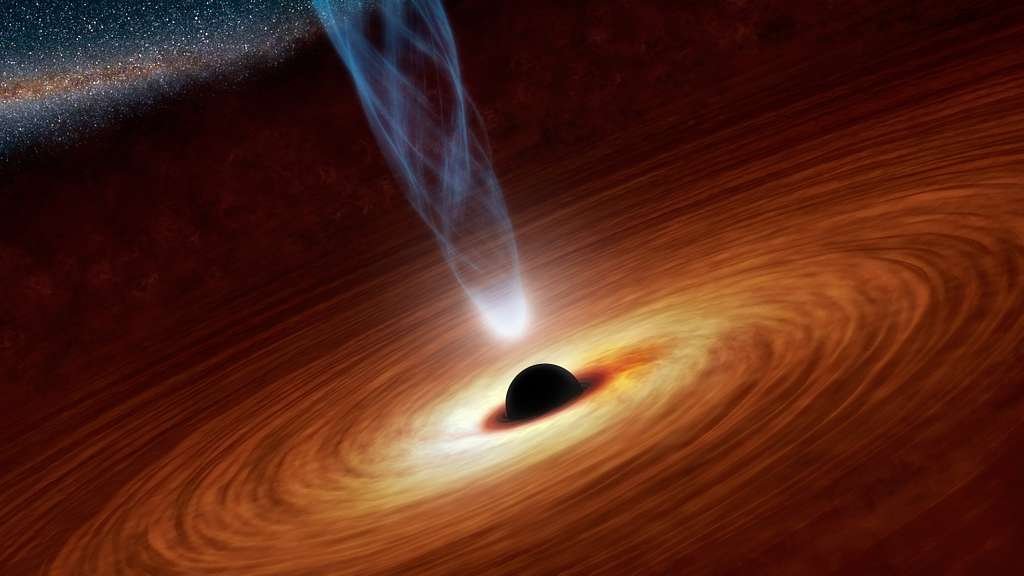

Stars, the celestial powerhouses scattered throughout the universe, play diverse and essential roles. They are the cosmic alchemists, forging elements through nuclear fusion that enrich the cosmos. The life and death of stars are pivotal events, influencing the composition of galaxies and seeding the universe with the building blocks of life. Black holes, enigmatic cosmic entities, exert gravitational forces so strong that not even light can escape their clutches. These cosmic vacuum cleaners, born from the remnants of massive stars, challenge our understanding of space and time. Neutron stars, with their extreme densities, further exemplify the cosmic extremes that celestial bodies can reach.
The Expanding Universe Theory
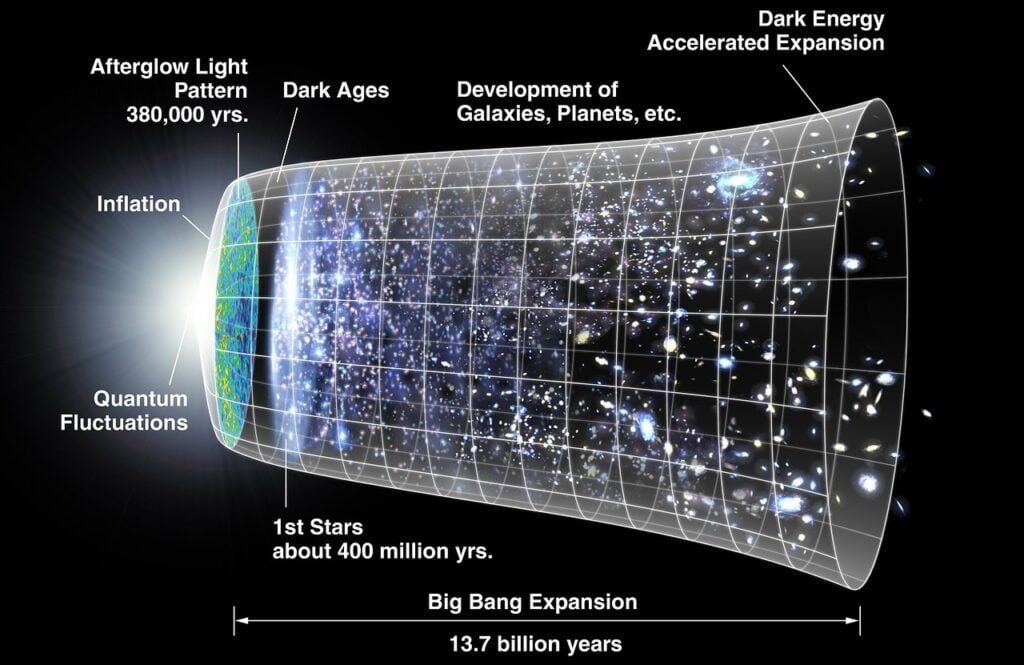
A paradigm-shifting concept in cosmology is the theory of the expanding universe. Observations of distant galaxies revealed that they are moving away from each other, suggesting that the fabric of space itself is expanding. This revelation transformed our understanding of the cosmos, implying that the universe had a beginning and has been evolving ever since.
The implications of an expanding universe are profound. It leads us to contemplate the origins of the cosmos in an event commonly known as the Big Bang. This cosmic genesis, where space and time emerged from a singular point, remains one of the most captivating and challenging ideas in cosmology.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
While the visible matter, the stars and galaxies we can observe, constitutes only a fraction of the universe, a vast majority remains hidden in the shadows. Dark matter, a mysterious form of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, exerts gravitational influence, revealing its presence through its subtle interactions. Dark energy, another enigmatic component, acts as a cosmic accelerator. Unlike gravity, which pulls matter together, dark energy drives the accelerated expansion of the universe. The dual mysteries of dark matter and dark energy underscore the profound gaps in our understanding of the universe’s composition.
The Birth and Death of Stars
Stars, as celestial entities, undergo a captivating life cycle that influences the evolution of galaxies. Stellar nurseries, regions rich in gas and dust, give birth to stars through gravitational collapse. These newborn stars shine brightly, radiating energy that shapes the surrounding cosmic landscape.
As stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they undergo transformations that can lead to spectacular events. Supernovae, the explosive deaths of massive stars, scatter heavy elements into space, enriching the interstellar medium. The remnants of these stellar explosions, including neutron stars and black holes, continue to influence the cosmic drama.
Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity
A cornerstone of our understanding of gravity and the fabric of space-time is Einstein’s theory of general relativity. This revolutionary theory, formulated in the early 20th century, describes gravity as the curvature of space-time caused by the presence of mass and energy.
The implications of general relativity extend from the cosmic scale to the minuscule realms of black holes. The bending of light around massive objects, known as gravitational lensing, provides a direct observational confirmation of Einstein’s predictions. Understanding general relativity is not just a scientific necessity; it is a gateway to unraveling the profound connections between space, time, and gravity.
Quantum Mechanics on a Cosmic Scale
While general relativity governs the macroscopic scale of the universe, quantum mechanics rules the microscopic world of particles. Even in the vastness of space, quantum principles come into play. The interplay between quantum mechanics and gravity becomes particularly relevant in the extreme conditions near black holes and during the early moments of the universe.
Quantum fluctuations, minuscule variations in energy at the quantum level, are thought to have played a role in the formation of cosmic structures. Understanding the quantum nature of the universe adds a layer of complexity to our exploration, bridging the gap between the infinitesimally small and the cosmically vast.
The Role of Light in Astronomy
In the cosmic quest for understanding, light becomes the messenger from the depths of space. Telescopes, our cosmic eyes, capture the faintest whispers of light emitted by distant celestial bodies. The analysis of this light provides astronomers with a wealth of information about the composition, temperature, and movement of the universe’s constituents. The cosmic journey of light is not without its challenges. Interstellar dust, gravitational lensing, and the expansion of the universe itself can alter the path of light, creating a cosmic tapestry that requires careful deciphering. The reliance on light as an astronomical tool underscores the intricate relationship between the universe and the electromagnetic spectrum.
Exoplanets and the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The discovery of exoplanets, planets orbiting stars beyond our solar system, opens a new chapter in the cosmic narrative. With thousands of exoplanets detected, scientists explore the conditions necessary for life beyond Earth. The search for habitable zones and the study of exoplanetary atmospheres provide tantalizing clues in the quest for extraterrestrial life.
While the detection of potentially habitable exoplanets sparks excitement, the search for life beyond our solar system remains a complex challenge. The exploration of exoplanets raises questions about the prevalence of life in the universe and the conditions required for its existence. The quest for extraterrestrial life adds a layer of anticipation to our understanding of the cosmic neighborhood.
Cosmic Phenomena: Supernovae, Nebulae, and Quasars
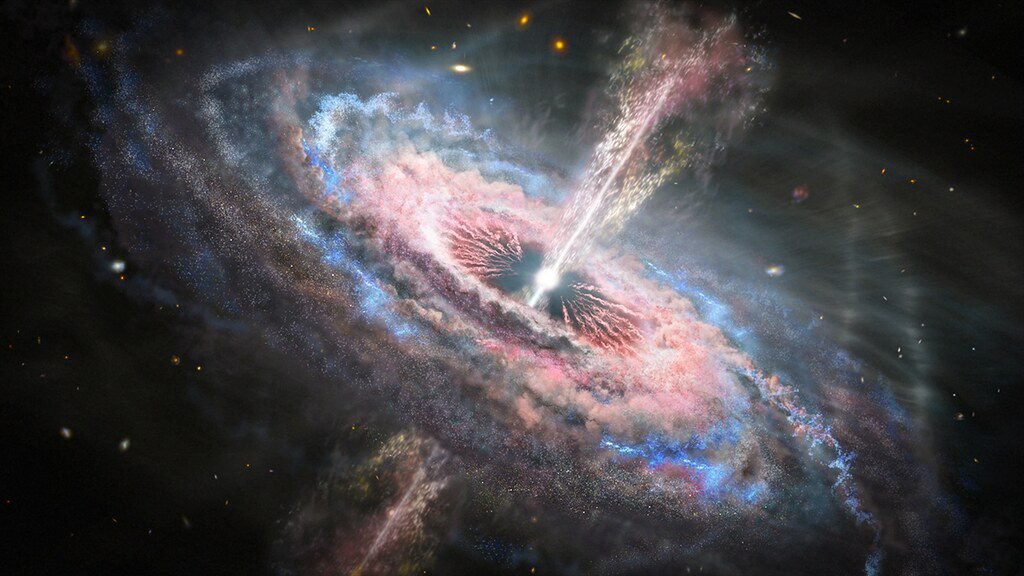

The universe is a theater of cosmic phenomena that captivate our imagination. Supernovae, the explosive deaths of massive stars, are cosmic fireworks that forge elements essential for life. Nebulae, vast clouds of gas and dust, serve as stellar nurseries where new stars are born, adding a poetic touch to the cosmic narrative. Quasars, luminous cores of distant galaxies, stand as celestial powerhouses that emit energy on a colossal scale. These enigmatic entities, powered by supermassive black holes, challenge our understanding of cosmic extremes. The study of cosmic phenomena provides a glimpse into the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the universe.
Time and Space Continuum
In the cosmic tapestry, time and space intertwine, creating a continuum that shapes the unfolding cosmic drama. The interplay of time and space, governed by the principles of general relativity, introduces a dynamic dimension to our perception of the universe.
The cosmic timeline stretches back to the early moments of the universe, from the hot, dense conditions of the Big Bang to the formation of the first galaxies. Understanding the continuum of time and space allows us to trace the cosmic evolution and witness the interconnected nature of the universe across vast cosmic scales.
Challenges in Understanding the Universe
While our cosmic journey has brought us remarkable insights, challenges persist in the quest to unravel the universe’s deepest secrets. Dark matter, dark energy, and the elusive nature of quantum gravity stand as formidable puzzles that demand innovative solutions.
The cosmic perplexities extend to the cosmic microwave background radiation, the relic radiation from the early universe, providing a snapshot of cosmic conditions when the universe was in its infancy. The quest for a unified theory that reconciles quantum mechanics and general relativity remains an open challenge, representing one of the frontiers of modern physics.
Conclusion: Embracing the Wonder of the Cosmos
As we conclude our odyssey through the cosmos, the overwhelming sense of wonder prevails. The universe, with its dazzling array of celestial wonders and perplexing enigmas, invites us to embrace the awe-inspiring beauty of the unknown. Our understanding of “How the Universe Works” is a testament to human curiosity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge that propels us to new cosmic frontiers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is the universe infinite?
- The true nature of the universe’s expanse remains an open question. While it may be vast, whether it is truly infinite is yet to be determined.
- What is dark matter, and why is it mysterious?
- Dark matter is a mysterious kind of stuff that doesn’t give off, take in, or bounce back light, making it puzzling and hard to figure out in the cosmos. Its nature remains elusive, and its existence is inferred from gravitational effects.
- How do astronomers study distant galaxies?
- Astronomers use telescopes and various tools to observe light emitted by distant galaxies. Analyzing this light provides insights into the composition, structure, and movement of galaxies.
- Are there other dimensions in the universe?
- The concept of other dimensions is theoretical and remains speculative. While some theories suggest the existence of extra dimensions, there is no direct empirical evidence.
- What happens inside a black hole?
- The interior of a black hole is a realm where the known laws of physics break down. It is a point of infinite density, known as a singularity, surrounded by an event horizon from which nothing can escape.
Enjoyed this informative article? Explore additional engaging and enlightening content here.



